- Report Review
- Posts
- Paper - Freelancing as a Career The Gig Economy - Parviz Izadi
Paper - Freelancing as a Career The Gig Economy - Parviz Izadi

Freelancing as a Career The Gig Economy
The gig economy is centered around achieving a balance between work and personal life. Over the years, the workforce has expanded due to increased access to education. At the same time, economic crises and downturns have made it difficult for many job seekers to secure stable and long-term employment. In response to these challenges, the gig economy has emerged as a major player in the job market.
The gig economy operates as a free-market system where businesses hire independent workers for short-term projects or service-based tasks. Imagine being a student who cannot commit to a full-time job; instead, you might start a podcast, become an influencer on TikTok promoting lifestyle products, teach kindergarten part-time, create designs and motion graphics for company social media pages, work for delivery platforms, trade assets, or take on various one-time or contractual jobs. Individuals who engage in such work are often referred to as "gig workers," "freelancers," or "independent contractors."
Every task a person takes on in this economy is considered “gig” This could be anything from completing a coding project via Upwork to creating YouTube content or even delivering a McDonald's order using Glovo. While these jobs generate income, they do not guarantee a fixed salary, especially in the long run. Gig workers lack traditional employment benefits such as health insurance, paid leave, or job security. To sustain themselves, they must continuously seek new opportunities to avoid periods of unemployment.
Ultimately, the gig economy offers flexibility and freedom, allowing individuals to choose when and how they work. However, it also comes with trade-offs, such as financial instability and the absence of long-term employment benefits1 .
The Gig Economy: Growing, not Ending
The gig economy continues to expand rather than fade away. When it comes to work-life balance, more people prefer the flexibility of working on a train with their laptop or heading to a new destination instead of being confined to an office. Some individuals have even turned their travels and experiences into a source of income by creating vlogs and sharing them on online platforms. Others who enjoy driving - like in the classic Taxi movie - find platforms like Uber to be a perfect fit. Social media influencers post their daily routines on Instagram while promoting products like shampoo or coffee machines. This shift benefits companies as well, allowing them to reduce office space, which leads to significant cost savings on rent, utilities, cleaning services, and even employee perks like coffee.
Demographic Trends
Just as China became a global manufacturing hub by producing goods at lower costs for Western markets, gig work has created similar economic advantages for workers in developing countries. Many freelancers in these regions prefer earning in USD or EUR, as it provides significantly higher purchasing power compared to local salaries.
For instance, in some of the most talent-rich developing countries - such as India, the Philippines, Bangladesh, and Pakistan - the average monthly wage ranges between $140 and $3802 . As a result, gig work offers an attractive alternative to traditional 9-to-5 jobs, allowing workers in these regions to earn more while working remotely for international clients.
In many countries, gig platforms serve as a "bridge employment" phase, allowing workers to gain experience before transitioning into permanent jobs. On the demand side, this market is driven by online startups, small businesses, and large corporations that hire gig workers for short- to medium-term projects. The rise of online freelancing platforms such as Upwork, and Fiverr has made it easier for companies to hire gig workers (also known as freelancers) from across the globe. Likewise, many independent workers join these platforms to offer their services to international clients.
Expecting the Unexpected
The gig economy also provides resilience in times of crisis. Imagine another global pandemic. Suddenly, working from home would be a necessity rather than a choice. While traditional jobs may struggle with an adaptation phase, gig workers already have an advantage, as remote work is their norm.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, freelance platforms like Upwork and Fiverr experienced a surge in demand, as reflected in their stock prices peaking in 2021. However, as the economy reopened and traditional jobs recovered, these platforms saw a significant decline. This trend highlights the gig economy's rapid adaptability to crises but also its vulnerability to economic cycles and market shifts3 .
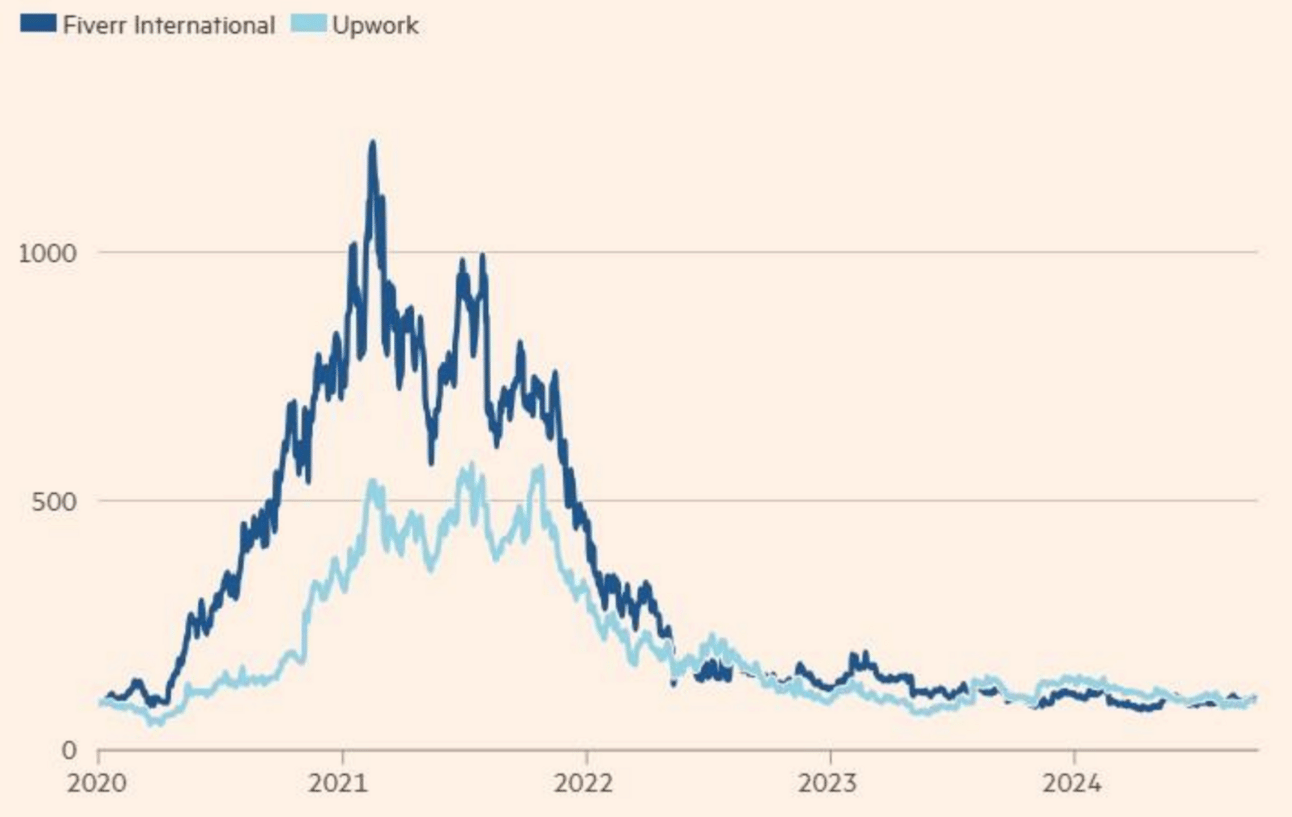
Source: Stephanie Stacey, Oct 8 2024, Online gig platforms focus on profits as workers return to office,
How Gig Platforms Operate
Gig economy platforms function by utilizing technology to efficiently connect service providers with clients. Individuals can register on these platforms either as freelancers offering services or as clients seeking specific tasks to be completed. The platform facilitates these interactions, manages transactions, and often handles payments typically charging a commission for its services.
For instance, a freelance writer on Upwork creates a profile highlighting their skills and experience, then bids on projects posted by clients. Once the work is completed and approved, the payment is processed through the platform. These platforms rely on algorithms to match freelancers with relevant job opportunities and incorporate rating and review systems to ensure trust and accountability within the marketplace4 .
Challenges
If you want the freedom to work from home, sleep in, and avoid rush-hour traffic, you need to take on more responsibility and use more mental energy. That’s because, as a freelancer, you’re not just doing the work, you’re also managing everything that comes with running your own business. Unlike a regular job where your boss or company handles many things for you, you’re now the one making sure everything stays on track.
One important aspect is taxes. Freelancers and gig workers are responsible for handling their own taxes, reporting their earnings, and making sure everything is done in order to avoid problems. Since there’s no employer to withhold taxes, it’s crucial to be aware of deadlines, required forms, and procedures. If it's affordable, hiring an accountant can be a good solution.
Retirement and health insurance are also key considerations. Even if you plan to sell your business in the future to fund your retirement, there are many uncertainties. Having a retirement account provides financial security and can also serve as a tax-efficient way to lower taxable income during high-earning years5 .
If you run a business that generates income but has no employees, you’re classified as self-employed. In that case, you can get health insurance through the individual Health Insurance Marketplace. Many companies provide a ‘death-in-service benefit’ to their employees. Life insurance ensures that if something happens to you, your family will have some financial stability6 .
Being part of a gig workers' community can be very helpful for finding job opportunities, choosing the right gigs, understanding market rates, and learning from others' experiences. Finding the right community could be challenging. These communities can exist on websites, forums, or even WhatsApp groups like those used by Uber drivers7 .
The Future Ahead
I. Regulations in Service for Freelancers
The European Parliament continuously keeps voting in favor of new rules aimed at improving working conditions for gig economy workers. The EU Platform Workers Directive seeks to:
correct the employment status of misclassified self-employed workers;
increase transparency in gig work;
regulate the use of algorithms and data in decision-making for platform workers8 .
Governments worldwide are also paying closer attention to the gig economy. Some regions are considering laws that would require companies to provide benefits to gig workers or reclassify them as employees to improve worker protections.
II. AI and freelancing
Artificial Intelligence is advancing rapidly, offering freelancers more support with workload management and automating routine tasks. AI tools can assist with:
Data entry;
Social media management;
Administrative tasks;
Project management;
Content creation.
With AI handling repetitive tasks, freelancers can focus on work that requires human expertise, such as client interactions, strategic planning, and creative projects. Emerging technologies like blockchain could also reshape the gig economy by improving job security, streamlining payments, and securing contracts9 .
III. Shift in Workforce Demographics
The gig economy is attracting a wide range of workers, from students and retirees to professionals looking for extra income. This shift is expanding job opportunities and shaping the demand for new skills in the market.
Benefits to the Economy
A shift to independent work increases labor productivity. It not only allows people to specialize in what they do best but also gives them the flexibility to focus on high-value tasks, leading to better job satisfaction and efficiency. Along with that, businesses are also restructuring jobs, splitting them between high-skill and low-skill workers, allowing for greater efficiency.
Capital productivity improves when independent workers use their personal assets - such as computers, smartphones, software, and even home office setups - to create and manage data, while those in logistics use personal vehicles, bicycles, and GPS-enabled apps to optimize deliveries.
Beyond traditional employees, retirees also stand to benefit from independent work. In the U.S., retirees make up 44% of the inactive population, while in Europe, they account for between 30% and 50%. Many retirees are willing to work but require flexible arrangements rather than full-time jobs. Platforms like HourlyNerd and SkillShare create opportunities for them to leverage their skills and experience, keeping them engaged in the workforce. This translates into additional working hours and higher GDP10 .
Conclusion
To conclude, it is argued that even those with regular jobs could consider pursuing independent work, as it offers numerous advantages. The continued expansion of independent work holds promises to boost employment opportunities, especially for those struggling to find traditional jobs. Digital platforms make it easier for individuals - whether retirees, freelancers, or unemployed job seekers - to find work suited to their skills.
However, it is important to acknowledge that not all gig workers enter the independent workforce by choice. Millions of workers in the U.S. and Europe prefer stable full-time jobs but cannot access them, leaving them dependent on gig work for survival.
Besides, many existing regulations were designed for a traditional workforce and fail to account for the realities of gig work. New labor policies and intermediary organizations such as unions or worker cooperatives are necessary to provide support and ensure fair treatment.
Another critical challenge is stimulating consumption, how gig platforms reshape consumer behavior and understanding the long-term economic impact of the gig economy. While gig platforms like Uber enable workers to earn and spend more, they may also shift purchasing patterns, reducing demand for major assets like personal cars. This shift could neutralize some of the economic gains from independent work, making it essential to continuously monitor these trends, analyze their effects, and adapt economic strategies accordingly as the gig economy evolves11 .
Resources
Pedrinha (Peddie) Furtado, The Gig Economy: An Overview Source:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_Asian_countries_by_average_wage
Roy, Gobinda & Shrivastava, Avinash. (2020). Future of Gig Economy: Opportunities and Challenges. 9. 14-25 Source: https://imikonnect.imik.edu.in/uploads/issue_file/3590503Mod_imiKonnect_January_March_2020.pdf#page=18
The Gig Economy: Shaping the Future of Work and Business (July 31, 2024). Available at: https://www.park.edu/blog/the-gig-economy-shaping-the-future-of-work-and-business/
Self-Employed Retirement Plans to Consider (Jan 3, 2025). Source:
https://www.nerdwallet.com/article/investing/retirement-plans-self-employed
Self-employed life insurance (Jan 7, 2025). Source:
https://www.legalandgeneral.com/insurance/life-insurance/guides/self-employed-life-insurance/
Source: https://freelancersunion.org/
Gig economy: how the EU improves platform workers rights (Apr 9, 2019). Source: https://www.europarl.europa.eu/topics/en/article/20190404STO35070/gig-economy-how-the-eu-improves-platform-workers-rights
Maricel Rivera, The Future of the Gig Economy: 2025 and Beyond (April 2, 2025).
Source: https://www.clearvoice.com/resources/gig-economy-future/
McKinsey Global Institute, Independent work: Choice, necessity, and the gig economy, (Oct 10, 2016). Source: https://www.mckinsey.com/featured-insights/employment-and-growth/independent-work-choice-necessity-and-the-gig-economy
Zac Abdulkadir, Exploring the Gig Economy: How Short-Term Jobs Are Reshaping the Workforce (Aug 20, 2024). Source: https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/exploring-gig-economy-how-short-term-jobs-reshaping-zac-t6ywe/